Ruby-throated Hummingbird (Archilochus colubris)
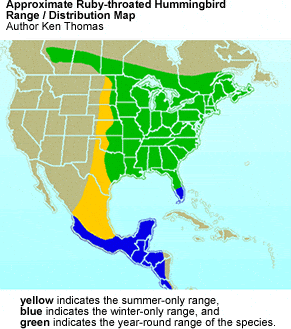
The Ruby-throated Hummingbirds (Archilochus colubris) are small hummingbirds that breed in southern Canada (central Alberta east to Nova Scotia) south to central and eastern USA (North Dakota east to Maine, and south to southern Texas.
Vagrants travel as far west as California. This species occupies the largest breeding range of any North American hummingbird.
They winter from central Mexico to western Panama in Central America. Some are year-round visitors in southern Florida.
During the spring and fall migrations, many of these tiny birds accomplish an amazing nonstop, 500-mile flight across the Gulf of Mexico. Considering that these tiny birds weigh as little as one US penny (the average male weighs even less), this is an impressive achievement.

?
Distribution / Range
Ruby-throated Hummingbirds are native to the following countries:
Bahamas, Belize, Bermuda, Canada, Cayman Islands, Costa Rica, Cuba, Dominican Republic, El Salvador, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Puerto RicoPuerto Rico, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Turks and Caicos Islands, and the United States.
They are accidental vagrants to
United States: The Ruby-throated Hummingbird is the only breeding hummingbird commonly found in the central and eastern half of the United States; and it is by far the most common species in that region – although most U.S. states report sporadic Ruby-throated Hummingbird sightings.
They have been recorded in the following U.S. States:
Alaska, Alabama, Arizona, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, District of Columbia / Washington, D.C, Florida, Idaho, Illinois, Mississippi, Missouri, Maine, North Dakota, Texas.
Canada: In south Canada, they occur in central Alberta east to Nova Scotia.
Migration Pattern

Habitat
During the winter, ruby-throated hummingbirds live in tropical deciduous forests, dry forests, second growth forests, forest edges, citrus groves, scrubland, hedgerows, along rivers and marshes – they basically occur in any semi-open habitat that offers suitable feeding locations
Their summer (breeding habitat) is similar to their wintering range. They are often found in mixed woodlands, eastern deciduous and pine forests, gardens, pastures and orchards. They remain close to the trees they nest in, while also having a supply of flowering plants and insects nearby for food.
Throughout its range, the Ruby-throated hummingbirds have adapted well to human development and readily take advantage of human-created garden habitats for feeding, shelter and nesting
Description and Similar Species

Calls / Vocalizations / Sounds
They make rapid, squeaky chirps mostly to threaten an intruder in their feeding territory. If this warning is ignored, he will chase the intruder out of his territory, potentially diving at him and striking him with his feet or his bill.
Lifespan
They can potentially live up to 12 years, provided they don’t meet an accidental death, or fall victim to predators or severe weather conditions.
The average lifespan, however, is more like 3 to 5 years.
The oldest wild ruby-throated hummingbird female lived at least 9 years (she was banded as a youngster and then caught again 9 years later).
The oldest known male lived 5 years. It is assumed that males don’t live as long as females as they spend so much energy defending their territories – in addition to the physical demands associated with their long migration to and from their breeding grounds.

Predation and Threats
Due to their small size, they are vulnerable to insect-eating birds and animals. They are preyed upon by larger birds, such as loggerhead shrikes, sharp-shinned hawks – even blue jays who will feed on their chicks. They are also preyed upon by bullfrogs, praying mantis (insects) or large orb-weaving spiders.
The most common predator of them all is most likely the common domestic cat. Other losses occur in urban / suburban areas because of collisions with windows.
Furthermore, this species depends heavily on specific forest plants for food, nesting and roosting. Habitat loss due to agricultural growth and clear-cutting of forests poses a major threat to their survival.
Status
They are quite common and its population is considered stable. Their numbers are estimated to be about 7,300,000.
In the 1800s, these birds were hunted for collection because of their small size and bright red feathers. Today, they are protected under the Migratory Bird Treaty between the U.S. and Canada; as well as by Appendix II of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species.
Ruby-Throated Hummingbirds Article by Ron Toel


Global Names
Chinese: ????? …
Czech: Kolibrík cervený, kolib?ík rubínohrdlý …
Danish: Rubinstrube …
Delaware: Lelèmbëlis …
Dutch: Robijnkeelkolibrie, Robijnkeeltje …
Estonian: rubiinkurk-koolibri …
French: Colibri à gorge rubis, Petit-Rubis, Wanga-nègès gòj wouj …
Finnish: Rubiinikurkkukolibri …
German: Rubin Kolibri, Rubinkehlkolibri, Rubinkolibri …
Italian: Colibrì golarubino …
Japanese: nodoakahachidori, ???????? …
Lithuanian: Raudongurklis kolibris …
Norwegian: Rubinstrupekolibri …
Ojibwa: ???????? ???? ? …
Polish: Koliber zwyczajny, koliberek rubinobrody …
Russian: ???????????? ?????????, ?????????????? ???????, ???????????? ??????? …
Slovak: cmelovec cervenohrdlý, Kolibrík rubínovokrký …
Spanish: Colibrí cuello de rubí, Colibrí de Garganta Rubí, Colibrí Garagnta de Rubí, Colibrí Garganta de Rubi, Colibrí garganta de rubí, Colibrí Garganta Rubí, colibrí ggarganta rubí, Colibrí Gorgirrubí, Colibrí Gorgirubí, Colibri Gorjirrubi, colibrí gorjirrubí, Estrellita Pasajera, Zumbador de Garganta Roja, Zumbador Migratorio, Zunzún de Paso …
Swedish: Rubinkolibri …
Hummingbird Resources
- Hummingbird Information
- Hummingbird Amazing Facts
- Attracting Hummingbirds to Your Garden
- Hummingbird Species
- Feeding Hummingbirds