Rheas
Rheas
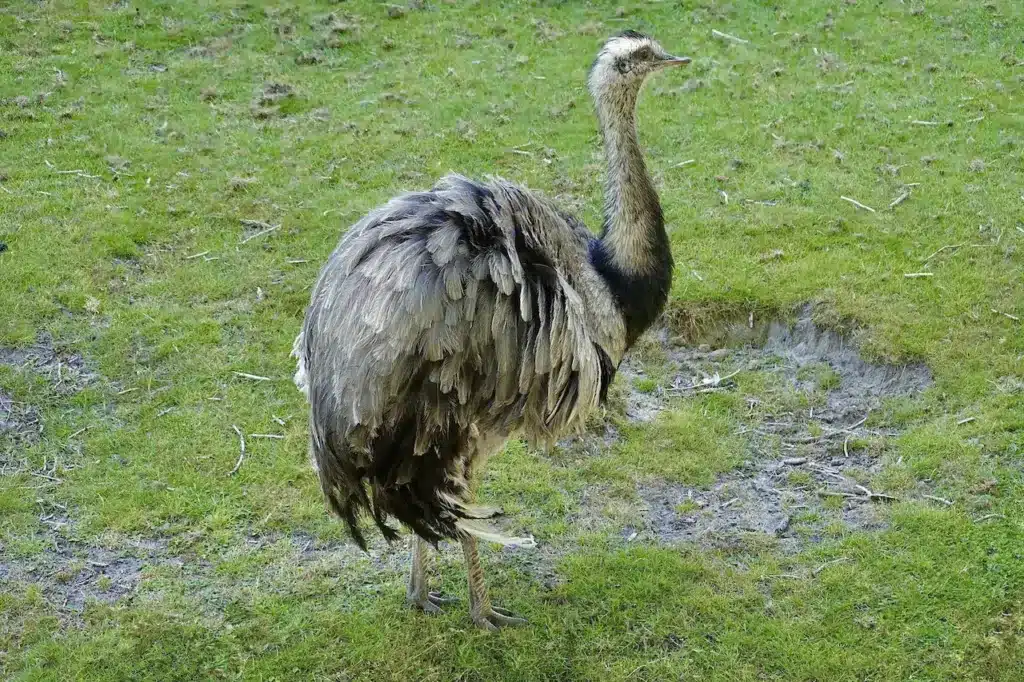
Rheas are large, flightless birds with gray-brown plumage, long legs, and long necks, similar to an ostrich.
These birds can reach 5.6 feet (1.7 m), and weigh up to 88 pounds (40 kg). Their wings are large for a flightless bird and are spread while running, to act like sails. Unlike most birds, rheas have only three toes. Their tarsus has horizontal plates on the front of it. They also store urine separately in an expansion of the cloaca.

Taxonomy
The recognized extant species are:
- Greater RheaRhea Americana
- R. a. Americana, found in campos of northern and eastern Brazil.R. a. intermedia, southeastern Brazil in Rio Grande do Sul and Uruguay.R. a. nobilis, eastern Paraguay, east of Rio Paraguay.R. a. araneipes, Chaco of Paraguay to Bolivia and Mato Grosso in Brazil.R. a. albescens, plains of Argentina south to Rio Negro.
- Lesser Rhea or Darwin’s RheaRhea pennata
- R. p. garleppi, puna of southeastern Peru, southwestern Bolivia, and northwestern Argentina.R. p. tarapacensis, northern Chile from Atacama to Tarapacá.R. p. pennata, Patagonian steppes in southern Argentina and southern Chile.
Rhea pennata was not always in the Rhea genus. In 2008 the SACC, the last holdout, approved the merging of the genera, Rhea and Pterocnemia on August 7, 2008. This merging of genera leaves only the Rhea genus.
A third species of rhea, Rhea nana, was described by Lydekker in 1894 based on a single egg found in Patagonia, but today no major authorities consider it valid.
Behavior
Individual and flocking
Rheas tend to be silent birds with the exception being when they are chicks or when the male is seeking a mate.
During the non-breeding season they may form flocks of between 10 and 100 birds, although the lesser rhea forms smaller flocks than this.
When in danger they flee in a zigzag course, utilizing first one wing and then the other, similar to a rudder. During breeding season the flocks break up.
Diet
They are omnivorous, preferring broad-leafed plants, but also eating seeds, roots, fruit, lizards, beetles, grasshoppers, and carrion.
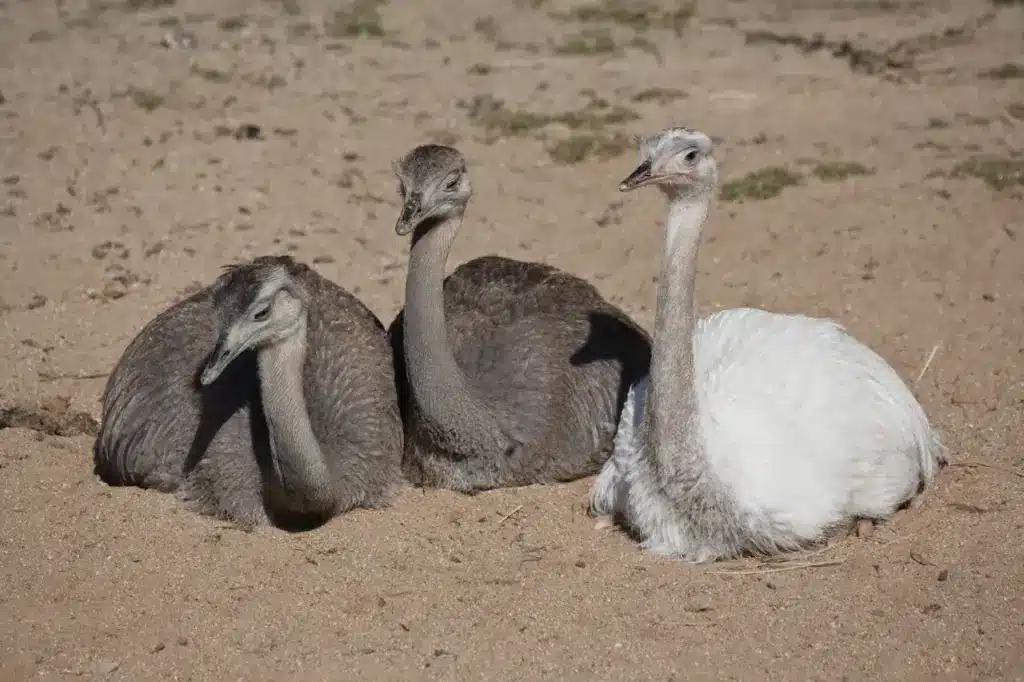

Reproduction
Rheas are polygamous, with males courting between two and twelve females.
After mating, the male builds a nest, in which each female lays her eggs in turn. The nest consists of a simple scrape in the ground, lined with grass and leaves.
The male incubates from ten to sixty eggs. The male will utilize a decoy system and place some eggs outside the nest and sacrifice these to predators, so that they won’t attempt to get inside the nest.
The male may utilize another subordinate male to incubate his eggs, while he finds another harem to start a second nest.
The chicks hatch within 36 hours of each other. The females, meanwhile, may move on and mate with other males. While caring for the young, the males will charge at any perceived threat that approach the chicks including female rheas and humans.
The young reach full adult size in about six months but do not breed until they reach two years of age.
Human interaction
Rheas have many uses in South America. Feathers are used for feather dusters, skins are used for cloaks or leather, and their meat is a staple to many people.